Home » Power BI Interview Questions and Answers
Are you preparing for a Microsoft Power BI interview and not sure what to expect? No worry we at EmergenTeck created a detailed guide that covers the most frequently asked Power BI interview questions and answers for both freshers and experienced professionals. Whether you’re preparing for your first job role or stepping into a senior position, this detailed of questions and answers with pdf and tutorials guide are designed to help you feel confident and ready. from core concepts to real-world implementation insights, you’ll find clear explanations that reflect the practical knowledge employers look for in top Power BI candidates.
What’s Included in the Interview Q&A Guide?
✅ Microsoft Power BI Interview Questions & Answers
✅ Questions for Freshers and Entry-Level Candidates
✅ Power BI Interview Questions for Experienced Professionals
✅ Key Concepts: Main Components of Power BI
✅ Topics on Database Automations and examples
✅ Overview of powerbi Framework
✅ Power BI Tutorials for Practical Learning
✅ Certification Guide with PDFs
✅ OnDemand Interview questions with answer & FAQ
In Import mode, data is imported and stored inside Power BI;trans ormations and visualizations work on he local copy. Scheduled refreshes update this data at intervals. DirectQuery connects live the source, allowing real-time data updates in reports but comes with some feature li itations and performance considerations.

Global settings affect all PowerBI reports on the desktop app, while Current File settings apply only to the specific Power BI project you are working on. This distinction helps manage configurations per user needs or per project.







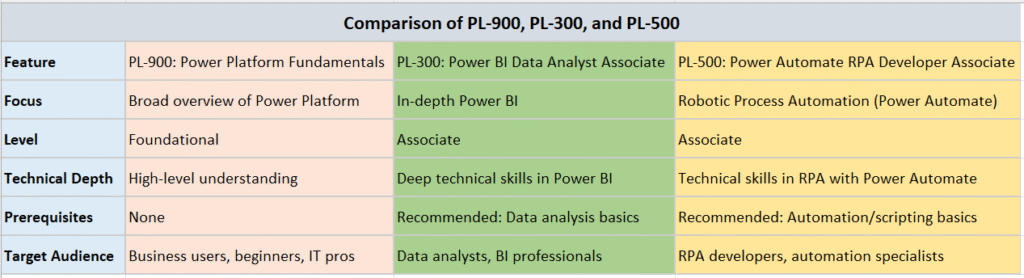
Bottom line: PL-900 is great for beginners, while PL-300 is ideal for those specializing in
Power BI. Choose based on your learning path and career goals.

WhatsApp us
Thanks for showing interest.
Please complete your registration process and your expert team will come back to you with Demo/Training details.